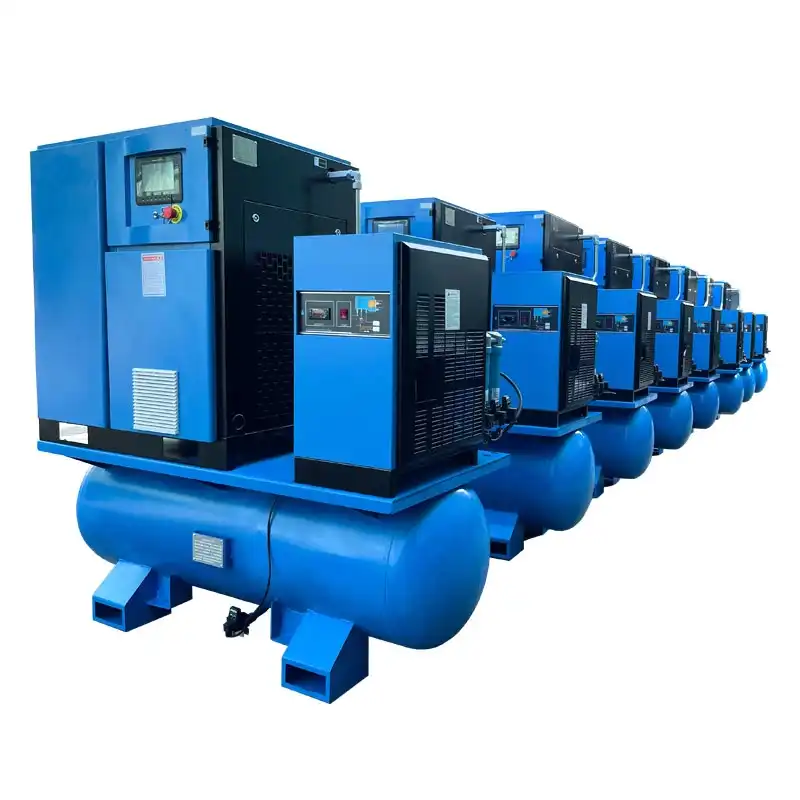
Product Description
Advantages:
Dry Oil-less Rocking piston Vacuum Pumps / Air Compressors
Pransch oilless dry rocking piston compressors and vacuum pumps have a variety of benefits, including:
- Performance: This small unit provides a high level of performance, bringing together characteristics of both diaphragm and piston air compressors.
- Clean air: These oil-free vacuum pumps are suitable for industries and settings where it’s important to avoid oil mist contamination, such as in hospitals and laboratories.
- Variety: Pransch rocking piston compressors are available in twin, single, tank-mounted and miniature styles for ideal use in a wide range of applications. Accessories provide additional versatility.
- Reliability: Made to withstand long-term use, the bearing assembly and piston rod are bonded together rather than clamped. This means they will not misalign, slip, loosen or come apart.
Oilless rocking pistons are particularly beneficial when it comes to optimal performance with very low maintenance.
| Model | Frequency | Flow | Pressure | Power | Speed | Current | Voltage | Heat | Sound | Weight | Hole | Installation Dimensions |
| Hz | L/min | Kpa | Kw | Min-1 | A | V | 0 C | dB(A) | Kg | mm | mm | |
| PM200C | 50 | 50 | 200 | 0.12 | 1380 | 0.45 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 48 | 1.8 | M5 | L100xW74 |
| 60 | 58 | 200 | 0.13 | 1450 | 0.90 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 48 | 1.8 | M5 | ||
| PM300C | 50 | 75 | 300 | 0.15 | 1380 | 0.76 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 45 | 3.2 | M6 | L118xW70 |
| 60 | 90 | 300 | 0.16 | 1450 | 1.52 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 45 | 3.2 | M6 | ||
| PM550C | 50 | 105 | 600 | 0.32 | 1380 | 1.50 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 56 | 6.0 | M6 | L148xW83 |
| 60 | 115 | 600 | 0.35 | 1450 | 3.00 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 56 | 6.0 | M6 | ||
| PM1200C | 50 | 120 | 300 | 0.45 | 1380 | 1.70 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 58 | 7.6 | M6 | L203xW86 |
| 60 | 145 | 300 | 0.49 | 1450 | 3.50 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 58 | 7.6 | M6 | ||
| PM1400C | 50 | 160 | 700 | 0.45 | 1380 | 1.70 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 58 | 8.5 | M6 | L203xW86 |
| 60 | 180 | 700 | 0.49 | 1450 | 3.50 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 58 | 8.5 | M6 | ||
| PM2000C | 50 | 230 | 800 | 0.55 | 1380 | 2.50 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 60 | 10.0 | M6 | L203xW86 |
| 60 | 250 | 800 | 0.60 | 1450 | 5.20 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 60 | 10.0 | M6 | ||
| HP2400C | 50 | 240 | 900 | 0.90 | 1380 | 3.30 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 75 | 17.0 | M7 | L246xW127 |
| 60 | 258 | 900 | 1.00 | 1450 | 6.80 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 75 | 17.0 | M7 | ||
| PM3000C | 50 | 250 | 1000 | 1.50 | 1380 | 4.20 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 76 | 17.5 | M7 | L246xW127 |
| 60 | 270 | 1000 | 1.70 | 1450 | 9.00 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 76 | 17.5 | M7 |
Why use a Rocking Piston Product?
Variety
Pransch oilless Rocking Piston air compressors and vacuum pumps, available in single, twin, miniature, and tankmounted
Styles, are the perfect choice for hundreds of applications. Choose from dual frequency, shaded pole,
And permanent split capacitor (psc) electric motors with AC multi-voltage motors to match North American,
European, and CHINAMFG power supplies. A complete line of recommended accessories as well as 6, 12, and
24 volt DC models in brush and brushless types are also available.
Performance
The rocking piston combines the best characteristics of piston and diaphragm air compressors into a small unit
With exceptional performance. Air flow capabilities from 3.4 LPM to 5.5 CFM (9.35 m3/h), pressure to 175 psi
(12.0 bar) and vacuum capabilities up to 29 inHg (31 mbar). Horsepowers range from 1/20 to 1/2 HP
(0.04 to 0.37 kW).
Reliable
These pumps are made to stand up through years of use. The piston rod and bearing assembly are bonded
Together, not clamped; They will not slip, loosen, or misalign to cause trouble.
Clean Air
Because CHINAMFG pumps are oil-free, they are ideal for use in applications in laboratories, hospitals, and the
Food industry where oil mist contamination is undesirable.
Pransch rocking piston compressors and vacuum pumps are used for many different applications, including:
- Medical: Surgical aspiration equipment, oxygen concentrators, ventilation equipment and eye surgery equipment.
- Dental: Portable dental equipment, dental vacuum ovens and dental compressors.
- Laboratory: Vacuum filtering, lab test equipment, vacuum centrifuge and body fluid analysis.
- Other applications: Diving air, vacuum food sealer, handicapped accessible doors, tire inflation equipment, vacuum mixing, automotive suspensions, paper counting machines, auto detailing equipment, core drilling, refrigerants reclamation, vacuum frames, dry sprinkler systems, cable pressurization and beverage dispensing.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-free |
|---|---|
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Structure Type: | Closed Type |
| Compress Level: | Single-Stage |
| Refrigerant Type: | Air |
| Material: | Steel |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
What Maintenance Is Required for Oil-Free Air Compressors?
Maintaining oil-free air compressors is crucial to ensure their optimal performance, reliability, and longevity. While oil-free compressors have lower maintenance requirements compared to oil-lubricated compressors, regular maintenance tasks are still necessary. Here’s a detailed explanation of the maintenance required for oil-free air compressors:
1. Regular Filter Replacements:
Oil-free air compressors have filters that help remove contaminants from the intake air. These filters should be regularly inspected and replaced as recommended by the manufacturer. Filters can become clogged over time, affecting the compressor’s efficiency and potentially increasing the risk of contaminants entering the compressed air stream. Regular filter replacements ensure proper air filtration and help maintain the desired level of air purity.
2. Condensate Drainage:
Oil-free compressors produce condensate, which is a mixture of water and oil-free compressed air. Proper condensate drainage is essential to prevent water buildup in the system, which can lead to corrosion and damage. Most oil-free compressors have automatic condensate drains that remove accumulated condensate. It’s important to regularly check and maintain these drains to ensure they are functioning correctly and prevent any blockages or leaks.
3. Inspection of Air Hoses and Connections:
Regularly inspecting air hoses, fittings, and connections is important to identify any leaks or damage. Leaks can lead to air pressure loss, reduced compressor efficiency, and increased energy consumption. Damaged hoses or connections should be repaired or replaced promptly to maintain the integrity of the compressed air system. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues early on and prevent costly breakdowns or inefficiencies.
4. Monitoring Air Pressure and Temperature:
Monitoring the air pressure and temperature of the compressor system is crucial for identifying any abnormalities or deviations from the desired operating parameters. Most oil-free compressors have built-in pressure and temperature sensors that provide real-time data. Regularly checking and recording this data can help detect any potential issues, such as pressure drops, abnormal temperature increases, or excessive cycling. If any abnormalities are detected, they should be investigated and addressed promptly to prevent further damage to the compressor.
5. General System Checks:
Performing general system checks on a regular basis helps ensure that all components of the oil-free air compressor are functioning properly. This includes inspecting the compressor motor, cooling fans, belts, and electrical connections. Any signs of wear, damage, or abnormal noise should be addressed promptly. Additionally, checking the compressor for any signs of oil contamination or unusual odors can help identify potential issues with the compressor system.
6. Manufacturer’s Recommendations:
It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and guidelines for the specific oil-free air compressor model. The manufacturer’s recommendations may include additional maintenance tasks specific to the compressor’s design and components. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that the compressor is properly maintained and can help prevent warranty issues.
Regular and proactive maintenance of oil-free air compressors is essential to ensure their reliable and efficient operation. Following the recommended maintenance tasks, monitoring system parameters, and promptly addressing any issues that arise can help extend the compressor’s lifespan, reduce the risk of breakdowns, and maintain the desired air quality for the intended applications.
.webp)
Are There Regulations Governing the Use of Oil-Free Air Compressors?
Yes, there are regulations governing the use of oil-free air compressors. Here’s a detailed explanation of the regulations and standards that apply to the use of oil-free air compressors:
1. Industry-Specific Regulations:
Depending on the industry and application, there may be specific regulations that govern the use of oil-free air compressors. For example:
- In the pharmaceutical industry, organizations such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe have guidelines and regulations regarding the use of compressed air in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. These guidelines often require the use of oil-free compressors to ensure the purity and integrity of the compressed air used in the production of drugs.
- In the food and beverage industry, regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have specific requirements for compressed air used in food and beverage processing. These regulations often mandate the use of oil-free compressors to prevent contamination of the final products.
- In the electronics industry, standards such as ISO 8573-1 specify the maximum allowable levels of various contaminants in compressed air used for electronic component manufacturing. These standards often necessitate the use of oil-free compressors to ensure the cleanliness and quality of the compressed air.
2. Air Quality Standards:
There are various air quality standards and classifications that dictate the acceptable levels of contaminants in compressed air. These standards help ensure that compressed air meets specific purity requirements for different applications. Examples of air quality standards include ISO 8573, which defines the purity classes for different contaminants in compressed air, and the Compressed Air and Gas Institute (CAGI) standards. Oil-free compressors are commonly used to meet the stringent requirements of these air quality standards, particularly in applications where oil contamination is not permissible.
3. Environmental Regulations:
Environmental regulations may also impact the use of oil-free air compressors. Oil-lubricated compressors can pose environmental risks if not properly managed. The release of oil into the environment can lead to soil and water contamination. To mitigate these risks, regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and similar agencies in other countries have regulations and guidelines in place to govern the use, handling, and disposal of lubricants and compressed air equipment. The use of oil-free compressors can help comply with these environmental regulations by eliminating the risk of oil contamination.
4. Occupational Health and Safety Regulations:
Occupational health and safety regulations may also apply to the use of oil-free air compressors. These regulations aim to protect workers from hazards associated with compressed air systems. They may cover aspects such as noise levels, vibration, electrical safety, and proper maintenance procedures. Compliance with these regulations helps ensure the safety and well-being of workers operating and maintaining the oil-free compressors and the associated compressed air systems.
It’s important to note that the specific regulations and standards governing the use of oil-free air compressors may vary depending on the country, industry, and application. It’s recommended to consult with regulatory authorities, industry associations, and relevant standards organizations to ensure compliance with the applicable regulations and standards in a particular context.
.webp)
Are Oil-Free Air Compressors More Environmentally Friendly?
Oil-free air compressors are considered more environmentally friendly compared to oil-lubricated air compressors. These compressors offer several features and advantages that contribute to their eco-friendly nature. Here’s a detailed explanation of why oil-free air compressors are considered more environmentally friendly:
1. Elimination of Oil Contamination:
One of the significant environmental benefits of oil-free air compressors is the elimination of oil contamination in the compressed air system. Oil-lubricated compressors require oil for lubrication, which can potentially leak or contaminate the compressed air. Oil contamination can have adverse effects on downstream equipment, processes, and the environment. In contrast, oil-free air compressors operate without oil, ensuring clean, oil-free compressed air and eliminating the risk of oil contamination.
2. Reduction of Oil Spills and Leaks:
Oil-lubricated compressors have a higher risk of oil spills or leaks due to the presence of lubricating oil in the system. Oil spills can have severe environmental consequences, polluting soil, water bodies, and ecosystems. Oil-free air compressors eliminate the risk of oil spills or leaks, as there is no oil used in the compression process. This reduces the potential harm to the environment and minimizes the need for costly cleanup efforts.
3. Energy Efficiency:
Oil-free air compressors can be more energy-efficient compared to oil-lubricated compressors. The absence of oil in the compression chamber reduces internal friction and mechanical losses, resulting in improved energy efficiency. Energy-efficient compressors consume less electricity, leading to reduced energy consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions. By using oil-free compressors, businesses can contribute to energy conservation and environmental sustainability.
4. Lower Environmental Footprint:
Due to the elimination of oil-related maintenance tasks, such as oil filtration, oil changes, and oil disposal, oil-free compressors have a lower environmental footprint. These maintenance activities associated with oil-lubricated compressors require the use of resources and generate waste, including used oil and oil filters. By using oil-free compressors, the consumption of resources and the generation of hazardous waste are reduced, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly operation.
5. No Oil Contamination in Air Tools and Products:
Oil contamination in compressed air can have detrimental effects on air tools, pneumatic equipment, and end products. Oil-free air compressors ensure that the compressed air delivered to these devices is clean and oil-free. This helps maintain the performance and longevity of air tools and prevents oil-related product defects. By using oil-free compressors, businesses can avoid costly repairs or replacements of equipment and minimize the risk of producing non-conforming or defective products.
It’s important to note that while oil-free air compressors offer environmental advantages, they may have certain limitations and considerations. These include the need for specialized maintenance, potential higher operating temperatures, and reduced maximum operating pressures compared to oil-lubricated compressors. Therefore, it’s essential to evaluate the specific requirements of the application and consider the trade-offs between environmental benefits and operational considerations when choosing an air compressor.


editor by CX 2024-04-24
China Standard Medical Oil Free Oil Silent Air Compressors Dental Oil-Free Air Compressor arb air compressor
Product Description
Specifications
1. Silent oil free
2. Electric of reducting energy
3. Durable working
4. High quality good price
5. Anti-rust for tank
pecifications Dental Air compressor:
1. Low noise
2. Oil less
3. Anti-rust for the tank after using for long time
4. Durable working time
5. High quality not easy broken
6. One years for warranty and life time for maintenance
7. Function for air drier or air cooling
Technical Data:
Rated voltage: 220VAC / 50HZ
Current: 2.4A
Power: 840W
Volume flow:105L/min
Starting pressure: 0.5Mpa
Rated discharge pressure: 0.77Mpa
Tank capacity: 32L/40L(CAN CHOSE 32L or 40L)
Noise :55-62dB
Weight: 32kg
Packing size: 42x42x68cm (carton)
| Tank capacity | 32L |
| Rated voltage | 220VAC / 50HZ |
| Power | 840W |
| Volume flow | 105L/min |
| Starting pressure | 0.5Mpa |
| Rated discharge pressure | 0.77Mpa |
| Noise | 55-62dB |
| G.W | 32kg |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Interface: | 4 Holes |
|---|---|
| Teeth Whitening Method: | Cold Light Whitening |
| Applicable Departments: | Oral Department of Internal Medicine |
| Certification: | ISO, CE |
| Type: | Air Compressor |
| Material: | Metal |
| Samples: |
US$ 165/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
Can Oil-Free Air Compressors Be Used for Breathing Air Applications?
Yes, oil-free air compressors can be used for breathing air applications, but it is crucial to ensure that the compressor and the associated equipment meet the required standards and regulations for breathing air quality and safety. Here’s a detailed explanation of using oil-free air compressors for breathing air applications:
1. Compressor Design and Certification:
When considering the use of oil-free air compressors for breathing air applications, it is essential to select compressors that are specifically designed and certified for such purposes. Dedicated oil-free compressors designed for breathing air applications typically incorporate additional features and safeguards to ensure the production of clean and safe compressed air. These compressors undergo rigorous testing and certification processes to meet the stringent standards and regulations for breathing air quality.
2. Air Treatment and Filtration:
In breathing air applications, the compressed air must undergo thorough treatment and filtration to remove contaminants and ensure its safety for breathing. Oil-free compressors are typically equipped with advanced filtration systems, including pre-filters, coalescing filters, activated carbon filters, and sometimes additional stages such as sterile filters or high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters. These filtration stages work together to eliminate particulates, moisture, odors, oil vapors, and other potential contaminants from the compressed air, ensuring its suitability for breathing air applications.
3. Compliance with Breathing Air Standards:
Oil-free compressors used for breathing air applications must comply with specific standards and regulations that define the acceptable limits for contaminants in breathing air. International standards such as ISO 8573 and national regulations, such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards in the United States, set guidelines for breathing air quality and specify the maximum allowable levels of contaminants, including oil content, particulate matter, and moisture. Compressors used for breathing air applications should meet or exceed these standards to ensure the safety and health of individuals who rely on the compressed air for breathing.
4. Regular Maintenance and Monitoring:
To ensure the ongoing safety and quality of the breathing air produced by oil-free compressors, regular maintenance and monitoring are essential. This includes routine inspections, filter replacements, and adherence to recommended maintenance schedules. Regular monitoring of air quality parameters, such as oil content, oxygen levels, and microbiological contamination, can help identify any potential issues and ensure that the compressor continues to produce clean and safe breathing air.
It’s important to note that not all oil-free compressors are suitable for breathing air applications. It is necessary to select compressors specifically designed and certified for this purpose, ensuring they meet the required standards and regulations. Additionally, the entire breathing air system, including air storage cylinders, distribution lines, and breathing apparatus, must also meet the necessary safety standards and undergo regular inspections and maintenance.
By following these guidelines and using appropriately designed and certified oil-free compressors, it is possible to generate clean and safe breathing air for various applications, such as medical facilities, diving operations, firefighting, and respiratory protection in industrial settings.
.webp)
Are There Any Specific Safety Considerations When Using Oil-Free Compressors?
Yes, there are specific safety considerations that should be taken into account when using oil-free compressors. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety considerations associated with oil-free compressor operation:
1. Electrical Safety:
Oil-free compressors are powered by electricity, so electrical safety measures should be followed. It is important to ensure that the compressor is properly grounded and connected to a suitable power source. Electrical wiring and connections should be inspected regularly to identify any potential hazards such as frayed wires or loose connections. Adequate circuit protection, such as fuses or circuit breakers, should be in place to prevent overloads or short circuits. All electrical work should be performed by qualified personnel in compliance with applicable electrical codes and regulations.
2. Pressure Safety:
Compressed air generated by oil-free compressors can reach high pressures, and proper pressure safety measures should be in place. Pressure relief valves are essential components that protect the compressor and the entire compressed air system from overpressurization. These valves should be properly sized, regularly inspected, and tested to ensure they operate within the specified pressure limits. Pressure gauges should be installed to monitor and display the pressure levels accurately. It is important to avoid exceeding the maximum pressure rating of the compressor and to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding pressure limitations.
3. System Ventilation:
Oil-free compressors generate heat during operation, and adequate ventilation is necessary to prevent overheating. Sufficient airflow around the compressor unit should be maintained to dissipate heat effectively. The compressor should be installed in a well-ventilated area, and any obstructions that could restrict airflow should be avoided. Inadequate ventilation can lead to increased operating temperatures, reduced compressor performance, and potential safety hazards. Manufacturers’ recommendations regarding ventilation requirements should be followed.
4. Preventing Injuries:
When working with oil-free compressors, certain precautions can help prevent injuries. It is important to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses, hearing protection, and gloves, when operating or maintaining the compressor. Loose clothing, jewelry, or other items that could get caught in moving parts should be avoided. Compressed air should never be directed towards the body or other individuals, as it can cause serious injuries, such as cuts, bruises, or even pneumothorax. Proper training and clear instructions for safe operation should be provided to all personnel working with the compressor.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of oil-free compressors are essential for safe operation. The compressor should be inspected for any signs of damage, leaks, or abnormal vibrations. Routine maintenance tasks, such as filter replacements, should be performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Maintenance procedures should be carried out with the compressor turned off and isolated from the power source. Only authorized personnel with the necessary training and knowledge should perform maintenance tasks on the compressor to ensure proper safety protocols are followed.
6. Emergency Preparedness:
Being prepared for potential emergencies is crucial when using oil-free compressors. Emergency shutdown procedures should be established and clearly communicated to all personnel. Adequate fire suppression equipment, such as fire extinguishers, should be readily available and properly maintained. In the event of a compressor-related incident, personnel should be trained on emergency response protocols and evacuation procedures.
It is important to consult the manufacturer’s documentation and guidelines for specific safety considerations related to the oil-free compressor model being used. Additionally, adherence to relevant safety regulations and standards, as well as regular safety training and awareness programs, further contribute to maintaining a safe working environment when using oil-free compressors.
.webp)
What Is an Oil-Free Air Compressor?
An oil-free air compressor, also known as an oilless air compressor, is a type of air compressor that operates without the use of lubricating oil in the compression chamber. Unlike traditional air compressors that rely on oil for lubrication and sealing, oil-free compressors employ alternative methods to achieve compression and deliver clean, oil-free compressed air. Here’s a detailed explanation of how oil-free air compressors work and their key characteristics:
Working Principle:
Oil-free air compressors utilize various techniques to compress air without the need for oil. The most common methods include:
- Dry Compression: In this method, the compression chamber doesn’t have any oil present. Special materials, coatings, and surface treatments are used to reduce friction and wear between the moving parts, allowing for efficient compression without oil lubrication.
- Water or Air Cooling: Oil-free compressors often employ advanced cooling mechanisms, such as water or air cooling, to dissipate the heat generated during compression. This helps to maintain the operating temperature within acceptable limits and ensures the longevity of the compressor.
- Piston Rings and Seals: Instead of relying on oil for lubrication and sealing, oil-free compressors use specialized piston rings, seals, or other forms of dry frictionless technology. These components provide the necessary sealing and reduce internal friction, allowing for efficient compression without the need for oil.
Characteristics of Oil-Free Air Compressors:
1. Clean and Oil-Free Air: The primary advantage of oil-free air compressors is that they deliver air that is free from oil contamination. This makes them suitable for applications where oil contamination can be detrimental, such as in the medical, pharmaceutical, food and beverage, electronics, and automotive industries.
2. Low Maintenance: Oil-free compressors typically require less maintenance compared to oil-lubricated compressors. Since there is no oil to change or monitor, maintenance tasks related to oil filtration, oil changes, and oil disposal are eliminated. This can result in cost savings and reduced downtime.
3. Compact and Lightweight: Oil-free compressors are often designed to be compact and lightweight, making them portable and easy to transport. This makes them suitable for applications where mobility is required, such as construction sites, workshops, and on-site maintenance tasks.
4. No Oil Contamination Risk: With oil-free compressors, there is no risk of oil contaminating the compressed air system. This eliminates the need for additional filtration or separation equipment to remove oil from the compressed air, simplifying the overall system design.
5. Lower Initial Cost: In general, oil-free compressors tend to have a lower initial cost compared to oil-lubricated compressors. This can be advantageous for applications with budget constraints or when the specific requirements of the application align with the capabilities of oil-free compressors.
It’s important to note that oil-free air compressors may have certain limitations compared to oil-lubricated compressors. They may have lower maximum operating pressures and higher operating temperatures. Additionally, the absence of oil lubrication may result in slightly reduced efficiency and increased wear on certain components over time.
By understanding the working principle and characteristics of oil-free air compressors, users can determine whether this type of compressor is suitable for their specific application and requirements.


editor by CX 2024-04-13
China best 150nm3/H 5bar Water or Air Cooled Oil-Free Reciprocating Helium Compressors air compressor portable
Product Description
25Nm3/h 200bar High Pressure Oil-free Helium Compressor CE Certified
Minwen high pressure industrial gas compressor belongs to oil-free reciprocating piston type construction. It is divided into three-stage, four-stage or five-stage compression according to the displacement and pressure. It is divided into air-cooled type and water-cooled type according to the cooling type.
An oil-free compressor is a type of gas compressor that operates without the need for lubricating oil in the compression chamber. Traditional gas compressors use oil to lubricate the moving parts and provide a better seal between the compression chamber and the piston or rotor. However, in certain applications where oil contamination is a concern, such as medical and dental facilities, food processing, electronics manufacturing, and painting, oil-free compressors are preferred.
There is no lubricating oil inside the gas compressors, grease lubricated sealing type bearing is adopted for the rotary moving components, the moving seals inside the cylinder are made of self-lubricating material so as to ensure that the compressed gas will never contact any oil.
Our Advantages
1. Oil-Free Gas: They deliver high-quality, oil-free compressed gases, which is essential in applications where oil contamination can be detrimental to the end product or process.
2. Reduced Maintenance: Oil-free compressors eliminate the need for oil changes, filter replacements, and oil disposal, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and costs.
3. Environmental Friendliness: The absence of oil reduces the risk of oil leaks or spills, making oil-free compressors environmentally friendly.
4. Improved gas Quality: Oil-free compressors provide cleaner gases, free from oil aerosols or vapors, which is essential in sensitive applications like medical and dental procedures or electronics manufacturing.
Features
Helium gas has a density that is 86% less than air. This means that the compressor has to be built to extremely tight tolerances to effectively compress helium gas without excessive blow-by. Furthermore, helium releases large amounts of heat when compressed, which the helium compressor must be able to absorb and shed. Thereore, for helium comoressors, we use water cooling for increased cooling efficiency.
Typical helium applications include recovery and compression systems for liquid cooling used in research institutions, particle accelerators, nuclear, medicine, aerospace, and militari missile applications. Helium recovery and compression is also used in general industrial applications, commercial merchant gas filing plants, heliostat applications, and helium mining, etc.
Company Profile
HangZhou Minwen Cryogenic Equipment Co., Ltd. is an established company specializing in industrial gas equipment and cryogenic solutions. With stable economy development in China, Minwen constantly strengthens its supply chain capabilities and resource integration capabilities. We are always on the way of promoting the efficiency and competitiveness, to guarantee high-quality performance of our services.
With advanced technologies and strict quality management, our products have passed the major international third-party quality control certifications such as ASME, CE, and Famous classification society such like BV, TUV, Lloyds and etc.
At Minwen, we pride ourselves on building long-lasting relationships with our clients. We will work with you every step of the way to ensure that your needs are met and your expectations are exceeded. We are committed to providing you with the best price and service we can offer, and we are confident in our ability to deliver top-quality solutions that cater to your specific set of requirements.
FAQ
1. Which countries you can ship the equipment to?
We ship to worldwide, such as Russia, Paraguay, Brazil, Colombia, Indonesia, Middle East, Africa, etc.
2. May I have the best price from you?
Sure. We are always on the way of promoting our competitiveness on products price and service.
3. Is your equipment quality good?
Yes. With advanced technologies and strict quality management, our products have passed the major international third-party quality control certifications such as ASME, CE, and Famous classification society such like BV, TUV, Lloyds
4. Do you provide one-stop service so I can save my time and labor?
Yes. Minwen constantly strengthens its supply chain capabilities and resource integration capabilities. You will own a professional team in China by cooperating with Minwen.
5. Where is your company located?
Our Export Office is located in HangZhou, with associated factories across China. This helps our international clients to integrate all the high quality resources together with Minwen.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Lifetime Aftersales Service |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Lifetime Aftersales Service |
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-free |
| Cooling System: | Water Cooling |
| Cylinder Arrangement: | Balanced Opposed Arrangement |
| Cylinder Position: | Vertical |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
Can Oil-Free Air Compressors Be Used for Breathing Air Applications?
Yes, oil-free air compressors can be used for breathing air applications, but it is crucial to ensure that the compressor and the associated equipment meet the required standards and regulations for breathing air quality and safety. Here’s a detailed explanation of using oil-free air compressors for breathing air applications:
1. Compressor Design and Certification:
When considering the use of oil-free air compressors for breathing air applications, it is essential to select compressors that are specifically designed and certified for such purposes. Dedicated oil-free compressors designed for breathing air applications typically incorporate additional features and safeguards to ensure the production of clean and safe compressed air. These compressors undergo rigorous testing and certification processes to meet the stringent standards and regulations for breathing air quality.
2. Air Treatment and Filtration:
In breathing air applications, the compressed air must undergo thorough treatment and filtration to remove contaminants and ensure its safety for breathing. Oil-free compressors are typically equipped with advanced filtration systems, including pre-filters, coalescing filters, activated carbon filters, and sometimes additional stages such as sterile filters or high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters. These filtration stages work together to eliminate particulates, moisture, odors, oil vapors, and other potential contaminants from the compressed air, ensuring its suitability for breathing air applications.
3. Compliance with Breathing Air Standards:
Oil-free compressors used for breathing air applications must comply with specific standards and regulations that define the acceptable limits for contaminants in breathing air. International standards such as ISO 8573 and national regulations, such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards in the United States, set guidelines for breathing air quality and specify the maximum allowable levels of contaminants, including oil content, particulate matter, and moisture. Compressors used for breathing air applications should meet or exceed these standards to ensure the safety and health of individuals who rely on the compressed air for breathing.
4. Regular Maintenance and Monitoring:
To ensure the ongoing safety and quality of the breathing air produced by oil-free compressors, regular maintenance and monitoring are essential. This includes routine inspections, filter replacements, and adherence to recommended maintenance schedules. Regular monitoring of air quality parameters, such as oil content, oxygen levels, and microbiological contamination, can help identify any potential issues and ensure that the compressor continues to produce clean and safe breathing air.
It’s important to note that not all oil-free compressors are suitable for breathing air applications. It is necessary to select compressors specifically designed and certified for this purpose, ensuring they meet the required standards and regulations. Additionally, the entire breathing air system, including air storage cylinders, distribution lines, and breathing apparatus, must also meet the necessary safety standards and undergo regular inspections and maintenance.
By following these guidelines and using appropriately designed and certified oil-free compressors, it is possible to generate clean and safe breathing air for various applications, such as medical facilities, diving operations, firefighting, and respiratory protection in industrial settings.
.webp)
Can Oil-Free Compressors Be Integrated into Existing Systems?
Yes, oil-free compressors can be integrated into existing systems in many cases. Here’s a detailed explanation of the integration possibilities and considerations when incorporating oil-free compressors into existing systems:
1. Compatibility:
Before integrating an oil-free compressor into an existing system, it’s important to assess the compatibility between the compressor and the system. Consider factors such as the required air pressure and flow rate, the electrical requirements, and the physical space available for installation. Compare these requirements with the capabilities and specifications of the oil-free compressor to ensure a suitable match.
2. Installation:
The installation process may vary depending on the specific system and compressor configuration. In some cases, it may be a straightforward replacement of the existing compressor with the oil-free compressor. However, certain modifications or adjustments may be necessary to accommodate the differences between oil-lubricated and oil-free compressors. For example, oil-free compressors may require additional filtration or moisture removal equipment to maintain the desired air quality. It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s installation guidelines and consult with qualified professionals if needed.
3. Piping and Connections:
When integrating an oil-free compressor into an existing system, the piping and connections need to be evaluated. The existing piping should be inspected for any potential issues such as leaks, corrosion, or inadequate sizing. Depending on the specific requirements of the oil-free compressor, modifications to the piping system may be necessary to ensure proper airflow, pressure drop, and connection compatibility. It’s crucial to ensure that the piping system can handle the air volume and pressure generated by the oil-free compressor without any restrictions or safety risks.
4. Control and Monitoring:
Integrating an oil-free compressor into an existing system may involve adjustments to the control and monitoring components. The control system should be capable of effectively operating and regulating the oil-free compressor based on the desired air pressure and flow requirements. This may require reprogramming or reconfiguring the control settings to accommodate the specific features and functionalities of the oil-free compressor. Additionally, monitoring systems should be updated to include relevant parameters specific to oil-free compressor operation, such as air purity levels or maintenance alerts.
5. Training and Familiarization:
When integrating an oil-free compressor into an existing system, it’s important to provide training and familiarization to the personnel responsible for operating and maintaining the equipment. The differences between oil-lubricated and oil-free compressors should be clearly explained, including any specific maintenance requirements or operational considerations. Training sessions can help ensure that the staff understands the new equipment and can effectively operate and maintain it in a safe and efficient manner.
6. Benefits and Considerations:
Integrating an oil-free compressor into an existing system offers several benefits. It can improve air quality, eliminate the risk of oil contamination, and enhance the performance and reliability of the compressed air system. However, it’s important to consider the initial investment costs, potential modifications required, and the overall compatibility with the existing system. Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis and consulting with experts can help determine the feasibility and potential advantages of integrating an oil-free compressor into the existing system.
In summary, oil-free compressors can generally be integrated into existing systems with proper assessment, planning, and installation procedures. Evaluating compatibility, ensuring appropriate installation, addressing piping and connection requirements, adjusting control and monitoring systems, providing adequate training, and considering the associated benefits and considerations are crucial steps in successfully integrating an oil-free compressor into an existing system.
.webp)
What Are the Advantages of Using Oil-Free Air Compressors?
Oil-free air compressors offer several advantages over their oil-lubricated counterparts. These compressors are designed to deliver clean, oil-free compressed air and provide benefits in various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages of using oil-free air compressors:
1. Clean and Oil-Free Air:
The primary advantage of oil-free air compressors is that they produce compressed air that is free from oil contamination. This makes them suitable for applications where oil-free air is crucial, such as in industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and painting. Oil-free compressed air ensures product quality, prevents contamination of sensitive equipment, and eliminates the risk of oil-related issues in downstream processes.
2. Reduced Maintenance:
Oil-free compressors generally require less maintenance compared to oil-lubricated compressors. Since there is no oil to change or monitor, maintenance tasks related to oil filtration, oil changes, and oil disposal are eliminated. This can result in cost savings, reduced downtime, and simplified maintenance schedules.
3. Elimination of Oil Contamination Risk:
With oil-free compressors, there is no risk of oil contaminating the compressed air system. This eliminates the need for additional filtration or separation equipment to remove oil from the compressed air. It simplifies the overall system design, reduces the risk of oil-related equipment failure, and minimizes the maintenance and associated costs.
4. Compact and Lightweight:
Oil-free compressors are often designed to be compact and lightweight, making them portable and easy to transport. This feature is advantageous for applications where mobility is required, such as construction sites, workshops, and on-site maintenance tasks.
5. Quiet Operation:
Oil-free compressors tend to operate at lower noise levels compared to oil-lubricated compressors. The absence of oil lubrication reduces the friction and mechanical noise, resulting in quieter operation. This makes oil-free compressors more suitable for noise-sensitive environments or applications where reduced noise levels are desired.
6. Environmental Considerations:
Oil-free air compressors are environmentally friendly due to the absence of oil. They eliminate the risk of oil spills or leaks that can harm the environment. Furthermore, oil-free compressors may require less energy consumption compared to oil-lubricated compressors, contributing to energy efficiency and reduced carbon footprint.
7. Lower Initial Cost:
In general, oil-free compressors tend to have a lower initial cost compared to oil-lubricated compressors. This can be advantageous for applications with budget constraints or when the specific requirements of the application align with the capabilities of oil-free compressors.
It’s important to note that oil-free air compressors may have certain limitations compared to oil-lubricated compressors. They may have lower maximum operating pressures and higher operating temperatures. Additionally, the absence of oil lubrication may result in slightly reduced efficiency and increased wear on certain components over time.
By considering these advantages, users can determine whether oil-free air compressors are suitable for their specific application and requirements.


editor by CX 2024-02-07
China supplier 45L/800W*2 Oil-Free Energy-Saving Compressors Portable Piston Air Compressor Top Quality Direct Driven Reciprocating Compressor with Best Sales
Product Description
Product Description
| MODEL | TL0160008 | TL0160571/TL0180571 | TL0160045/TL0180045 | TL0160058/TL0180058 |
| INPUT POWER | 600W | 600W/800W | 600W*2/800W*2 | 600W*3/800W*3 |
| RATED/VOLTAGE | 200-240V/50HZ | 200-240V/50HZ | 200-240V/50HZ | 200-240V/50HZ |
| RATED SPEED | 1450RPM | 1450RPM | 1450RPM | 1450RPM |
| WORK PRESSURE | 8BAR/116PSI | 8BAR/116PSI | 8BAR/116PSI | 8BAR/116PSI |
| TANK VOLUME | 8L/2.0GAL | 22L/5.8GAL | 45L/12.0GAL | 58L/15.3GAL |
| AIR DISPLACEMENT | 3.8CFM/107L/MIN | 3.8CFM/107L/MIN 4.6CFM/139L/MIN |
7.6CFM/107L/MIN 9.2CFM/139L/MIN |
11.4CFM/107L/MIN 13.8CFM/387L/MIN |
Company Information
FAQ
Package Delivery
Click Here For More Products
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-free |
|---|---|
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Structure Type: | Open Type |
| Compress Level: | Single-Stage |
| Capacity: | 139L/Min |
| Core Component: | Motor |
| Samples: |
US$ 119/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.webp)
Can air compressors be used for shipbuilding and maritime applications?
Air compressors are widely used in shipbuilding and maritime applications for a variety of tasks and operations. The maritime industry relies on compressed air for numerous essential functions. Here’s an overview of how air compressors are employed in shipbuilding and maritime applications:
1. Pneumatic Tools and Equipment:
Air compressors are extensively used to power pneumatic tools and equipment in shipbuilding and maritime operations. Pneumatic tools such as impact wrenches, drills, grinders, sanders, and chipping hammers require compressed air to function. The versatility and power provided by compressed air make it an ideal energy source for heavy-duty tasks, maintenance, and construction activities in shipyards and onboard vessels.
2. Painting and Surface Preparation:
Air compressors play a crucial role in painting and surface preparation during shipbuilding and maintenance. Compressed air is used to power air spray guns, sandblasting equipment, and other surface preparation tools. Compressed air provides the force necessary for efficient and uniform application of paints, coatings, and protective finishes, ensuring the durability and aesthetics of ship surfaces.
3. Pneumatic Actuation and Controls:
Air compressors are employed in pneumatic actuation and control systems onboard ships. Compressed air is used to operate pneumatic valves, actuators, and control devices that regulate the flow of fluids, control propulsion systems, and manage various shipboard processes. Pneumatic control systems offer reliability and safety advantages in maritime applications.
4. Air Start Systems:
In large marine engines, air compressors are used in air start systems. Compressed air is utilized to initiate the combustion process in the engine cylinders. The compressed air is injected into the cylinders to turn the engine’s crankshaft, enabling the ignition of fuel and starting the engine. Air start systems are commonly found in ship propulsion systems and power generation plants onboard vessels.
5. Pneumatic Conveying and Material Handling:
In shipbuilding and maritime operations, compressed air is used for pneumatic conveying and material handling. Compressed air is utilized to transport bulk materials, such as cement, sand, and grain, through pipelines or hoses. Pneumatic conveying systems enable efficient and controlled transfer of materials, facilitating construction, cargo loading, and unloading processes.
6. Air Conditioning and Ventilation:
Air compressors are involved in air conditioning and ventilation systems onboard ships. Compressed air powers air conditioning units, ventilation fans, and blowers, ensuring proper air circulation, cooling, and temperature control in various ship compartments, cabins, and machinery spaces. Compressed air-driven systems contribute to the comfort, safety, and operational efficiency of maritime environments.
These are just a few examples of how air compressors are utilized in shipbuilding and maritime applications. Compressed air’s versatility, reliability, and convenience make it an indispensable energy source for various tasks and systems in the maritime industry.
.webp)
How are air compressors used in refrigeration and HVAC systems?
Air compressors play a vital role in refrigeration and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, providing the necessary compression of refrigerant gases and facilitating the heat transfer process. Here are the key ways in which air compressors are used in refrigeration and HVAC systems:
1. Refrigerant Compression:
In refrigeration systems, air compressors are used to compress the refrigerant gas, raising its pressure and temperature. This compressed gas then moves through the system, where it undergoes phase changes and heat exchange to enable cooling or heating. The compressor is the heart of the refrigeration cycle, as it pressurizes and circulates the refrigerant.
2. Refrigeration Cycle:
The compression of refrigerant gas by the air compressor is an essential step in the refrigeration cycle. After compression, the high-pressure, high-temperature gas flows to the condenser, where it releases heat and condenses into a liquid. The liquid refrigerant then passes through an expansion valve or device, which reduces its pressure and temperature. This low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant then enters the evaporator, absorbing heat from the surrounding environment and evaporating back into a gas. The cycle continues as the gas returns to the compressor for re-compression.
3. HVAC Cooling and Heating:
In HVAC systems, air compressors are used to facilitate cooling and heating processes. The compressor compresses the refrigerant gas, which allows it to absorb heat from the indoor environment in the cooling mode. The compressed gas releases heat in the outdoor condenser unit and then circulates back to the compressor to repeat the cycle. In the heating mode, the compressor reverses the refrigeration cycle, absorbing heat from the outdoor air or ground source and transferring it indoors.
4. Air Conditioning:
Air compressors are an integral part of air conditioning systems, which are a subset of HVAC systems. Compressed refrigerant gases are used to cool and dehumidify the air in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. The compressor pressurizes the refrigerant, initiating the cooling cycle that removes heat from the indoor air and releases it outside.
5. Compressor Types:
Refrigeration and HVAC systems utilize different types of air compressors. Reciprocating compressors, rotary screw compressors, and scroll compressors are commonly used in these applications. The selection of the compressor type depends on factors such as system size, capacity requirements, efficiency, and application-specific considerations.
6. Energy Efficiency:
Efficient operation of air compressors is crucial for refrigeration and HVAC systems. Energy-efficient compressors help minimize power consumption and reduce operating costs. Additionally, proper compressor sizing and system design contribute to the overall energy efficiency of refrigeration and HVAC systems.
By effectively compressing refrigerant gases and facilitating the heat transfer process, air compressors enable the cooling and heating functions in refrigeration and HVAC systems, ensuring comfortable indoor environments and efficient temperature control.
.webp)
Can air compressors be used for automotive applications?
Yes, air compressors can be used for various automotive applications and are commonly found in automotive repair shops, garages, and even in some vehicles. Here are some automotive applications where air compressors are frequently utilized:
1. Tire Inflation: Air compressors are commonly used to inflate tires in automotive applications. They provide a convenient and efficient way to inflate tires to the recommended pressure, ensuring optimal tire performance, fuel efficiency, and safety.
2. Air Tools: Air compressors power a wide range of pneumatic tools used in automotive repair and maintenance. These tools include impact wrenches, ratchet wrenches, air hammers, pneumatic drills, and sanders. Air-powered tools are favored for their high torque and power-to-weight ratio, making them suitable for heavy-duty automotive tasks.
3. Spray Painting: Air compressors are commonly used in automotive painting applications. They power airbrushes and spray guns that are used to apply paint, primer, and clear coats. Air compressors provide the necessary air pressure to atomize the paint and deliver a smooth and even finish.
4. Brake System Maintenance: Air compressors play a crucial role in maintaining and diagnosing automotive brake systems. They are used to pressurize the brake lines, allowing for proper bleeding of the system and detection of leaks or faults.
5. Suspension Systems: Some automotive suspension systems, such as air suspensions, rely on air compressors to maintain the desired air pressure in the suspension components. The compressor inflates or deflates the suspension as needed to provide a comfortable ride and optimal handling.
6. Cleaning and Dusting: Air compressors are used for cleaning automotive parts, blowing away dust and debris, and drying surfaces. They provide a high-pressure stream of air that effectively cleans hard-to-reach areas.
7. Air Conditioning Systems: Air compressors are a key component in automotive air conditioning systems. They compress and circulate refrigerant, allowing the system to cool and dehumidify the air inside the vehicle.
When using air compressors for automotive applications, it’s important to consider the specific requirements of the task at hand. Ensure that the air compressor has the necessary pressure and capacity to meet the demands of the application. Additionally, use appropriate air hoses, fittings, and tools that are compatible with the compressor’s output.
Overall, air compressors are versatile and valuable tools in the automotive industry, providing efficient power sources for a wide range of applications, from tire inflation to powering pneumatic tools and supporting various automotive systems.


editor by CX 2023-10-17
China Good quality Gold Supplier CZPT 2 Bar 3 Bar 4 Bar 5 Bar Low Pressure Water-Injected Oil-Free Single Screw Type Air Compressors with CE & ISO Certificate with Great quality
Product Description
2~40bar DIRECT-DRIVE WATER-INJECTED OIL-FREE SCREW AIR COMPRESSOR (PM VSD)
1. Low temperature means more efficiency
With an exceptionally low running temperature of less than 60ºC, near isothermal compression is achieved.
The superior cooling capability of water removes the heat and gives more air per kW of power.
This also eliminates the need for an internal cooler and aftercooler, the associated power consumption reduces pressure drop to a minimum.
2. Cutting the maintenance cost
Spare parts only need air filter elements and water filter elements
Low operating temperature ensures the long service life of the screw air end, avoiding expensive maintenance costs for the screw rotor.
Low temperature reduces the stress on other components ensuring long life.
3. Avoiding the costs of extra energy to combat pressure drop
These costs, although not apparent at the time of purchase, are very high and contribute substantially to the total cost of ownership.
4. No Gearbox No need for associated oil lubrication.
5. Simple structure
Fewer moving parts than the dry oil-free screw air compressor, meaning there is less to go wrong,
while balance bearing loads extend the compression element service life for low-cost operation.
Product Parameters
Product Description
Company Profile
Hot Sale Products
2~10bar Oil-injected 7~16bar All-in-1 Small Single-phase
Screw Air Compressor Screw Air Compressor Screw Air Compressor
2~40bar 100% Oil-free 8~12bar 100% Oil-free Diesel Engine Portable
Screw Air Compressor Scroll Air Compressor Screw Air Compressor
Main Product
What we can supply:
* Oil-injected Screw Air Compressor (2~16 bar)
* All-in-1 Screw Air Compressor with Tank, Dryer, and Filters (7~16 bar)
* Single-phase Small Screw Air Compressor for Home use (8~10 bar)
* Water-injected Oil-free Screw Air Compressor (2~40 bar)
* Oil-free Scroll Air Compressor (8~12 bar)
* Diesel&Electric Engine Portable Screw Air Compressor (8~30 bar)
* Air Dryer, Air tank, Filters, and other Spare parts
| After-sales Service: | 24*7 Online Services and Video Guide |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year for The Whole Machine & 2 Years for Air End |
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-free |
| Cooling System: | Air Cooling |
| Power Source: | AC Power |
| Installation Type: | Stationary Type |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Choose an Air Compressor for Your Business
There are several factors to consider when choosing an air compressor for your business. One factor to consider is the type of compressor you are looking for, which may include single-stage, low noise, and positive displacement. Hope this article helps you make the right decision. After all, your business success will depend on this device! Let’s take a closer look at these factors. Also, consider what compressor manufacturers say about their products.
Positive displacement
Positive displacement air compressors compress air by drawing in a volume from an inlet and extruding it out of a chamber. This increases the pressure at which the gas can be pumped at rates that cannot be pumped through the outlet at lower pressures at higher mass flow rates. These types of compressors are available in single-acting and double-acting configurations. They are classified by the number of cylinders.
There are two different types of air compressors: reciprocating air compressors and screw compressors. Both are roll machines. Positive displacement air compressors use pistons and cylinders to compress air. The resulting air pressure builds up within the compressor housing, increasing the potential energy of the compressed air. Screw air compressors are the most popular positive displacement air compressors, which can be either single-stage screw-blade air compressors or multi-stage screw-blade oil-immersed screw air compressors.
Positive displacement flowmeters use a rotating measuring chamber to divide the fluid into discrete quantities. The number of times the chamber was refilled and emptied was used to estimate the total flow. However, positive displacement flow meters are prone to leaks, reducing the accuracy of the estimates. If a leak occurs, it can cause false readings and damage the compressor. However, leaks in positive displacement air compressors can reduce pressure.
The most common types of positive displacement air compressors are screw, reciprocating, and vane. Rotary positive displacement air compressors are also available as well as many other air compressors. Positive displacement air compressors are most commonly used in large manufacturing facilities. If you are considering an air compressor for commercial or industrial applications, it is imperative to understand how the components of the unit work. Please read the information below to learn more before deciding which application is best for you.
Positive displacement air compressors use a piston to force air into a chamber, compressing the air in the process. The piston moves in the opposite direction, thereby reducing the volume of the chamber. When the amount of air in the chamber reaches its maximum value, the valve opens, allowing it to escape at higher pressure. Positive displacement air compressors are generally less efficient than centrifugal compressors. However, they are still an excellent choice for a variety of applications.
Single-stage
The discharge pressure of the single-stage air compressor is used to control the operation of the compressor. Properly designed load/unload controls allow the air compressor to operate at its most efficient point while minimizing stress on the main engine bearings. Single-stage air compressors can approach variable speed efficiency with appropriate storage capacity. However, improper storage can cause premature bearing wear on the main unit. If this is the case, a single-stage air compressor may not be ideal.
A single-stage air compressor has only one cylinder, which means one stroke is required to move air from one cylinder to another. Pressure is measured in cubic feet per minute or CFM. Tank size is also important as a large single-stage air compressor may be required to operate multiple air tools. Single-stage air compressors can be used in a variety of applications and can last for years.
For the most common uses, single-stage air compressors are the most practical option. These devices work with most hand tools, from hammers to grinders. Single-stage air compressors are lightweight and easy to move. However, two-stage air compressors provide more CFM, making them a better choice for industrial or commercial use. However, two-stage compressors are not suitable for private use. Therefore, if your main purpose is DIY and craft projects, it is better to choose a single-stage air compressor.
Compared with two-stage air compressors, single-stage screw air compressors are cheaper. They come from a variety of manufacturers and range in power from 3 to 600 horsepower. Single-stage air compressors are a cost-effective solution for a variety of air compressor needs. They offer flexibility and multiple control methods, making them an excellent choice for many different applications. Therefore, when choosing an air compressor for your business, choose the one with the most suitable functions.
Single-stage air compressors are the most affordable and easy-to-use air compressors for small to medium jobs. They also have higher compression ratios. The compression ratio is the ratio of absolute discharge pressure to absolute inlet pressure. When calculating the ratio, it takes into account atmospheric pressure and gauge pressure. The compression ratio pushes the surface area of the rotor, which increases the thrust load.
Single-stage air compressors are smaller and easier to transport than two-stage units. Single-stage air compressors have one air intake, and two-stage air compressors have two air intakes. The difference between single-stage and two-stage air compressors largely depends on the number of times the air is compressed. A single-stage air compressor compresses the air once, while a dual-stage air compressor compresses the same amount of air twice.
low noise
Low noise air compressors are ideal for a variety of applications. While no air compressor is completely silent, some models are much quieter than others. For the Hitachi EC28M portable compressor, the noise level is 59 decibels. The compressor features steel rollers that protect the internal components and give it a sleek, modern look. It also has a one-gallon fuel tank and a half-horsepower drive.
Noise from air compressors can be distracting and reduce productivity. It is important to choose low-noise air compressors to keep employees healthy and happy at work. While noise is an unfortunate aspect of working on the shop floor, reducing it can improve productivity. By reducing distracting noise, employees can focus on their work and communicate more effectively. That means higher quality work and happier clients. If you’re looking for a low-noise air compressor, be sure to read the tips below.
Low noise air compressors are an excellent choice for businesses of all sizes. These powerful tools can run multiple tools simultaneously. The two water tanks are made of rust-resistant aluminum and are stackable. This air compressor is heavier and can handle large jobs with ease. It costs more than other air compressors, but it can handle a lot of work efficiently. CZPT Air Tools air compressors come with a one-year warranty and are highly recommended by contractors.
Noiseless air compressors are generally more expensive than comparable products, but they are worth the extra cost. Noiseless compressors are a good option for businesses that need to avoid disturbing nearby people. For example, you might want to consider a low-noise air compressor for a dental office, which cannot tolerate noise. Fortunately, this problem can be solved by relocating the compressor to a location that is more isolated from your workspace.
One brand of low-noise air compressors offers two models. The CZPT Air Tools 2010A features a large cast aluminum can, regulating pressure gauge, and two universal quick-connects. It produces 68 decibels of noise when it works. It has a large 8-gallon fuel tank capacity and has wheels and handles for easy transport. Its powerful engine produces a low noise level of 68 decibels.
Another popular low noise air compressor is the Makita MAC210Q Quiet Series. This model is capable of producing up to 71.5 decibels of sound, which is the amount of air it produces at 90PSI. The MAC210Q features a durable oil-free pump and weighs just 36 pounds with a handle and wheels. These compressors are easy to move and ideal for indoor work.

editor by CX 2023-06-05